Table of Contents

SDF Dial-up via pppconfig and pon|poff|plog on Ubuntu
Introduction:
There are several ways to setup a PPP-based dial-up network connection on Linux. This tutorial illustrates setting up such a connection using pppconfig on Ubuntu Linux. Once set up, regular users can start, stop and monitor the network connection via pon, poff and plog. All of these tools are console-based and the initial setup requires the user to invoke superuser privileges via the sudo command.
Prerequisites:
Verify that the modem is installed correctly and that pppconfig, pon, poff and plog are present on your system (all should be part of the base Ubuntu install). The which command is useful for this: ie. which pppconfig should return /usr/sbin/pppconfig. Also have your SDF Dial-up account information at hand: username, password, local access number. See FAQ>DIALUP for details.
A word about modems: most internal modems are “WinModems” (MS Windows only) and will not likely work with Linux; the best option is an external “hardware modem” that connects via a serial or USB port. Such modems contain their own controller chip (hence the term “hardware modem”) and do not rely on special drivers to function. That said, if all you have is a WinModem it is possible that someone has created a Linux driver for it; check at linmodems.org to see if yours is supported.
Basic Setup:
Open a terminal window (click Applications>Terminal ; maximize window) and invoke pppconfig using the sudo command:
# mr_retro@rustbucket:~$ sudo pppconfig [sudo] password for mr_retro:
pppconfig should launch ; it's a curses-based application that uses the TAB and Up/Down Arrows to move between fields, SPACE to toggle fields on/off and ENTER to select. The following screens show an account call SDF_dialup being set up for a 56K external modem installed on serial port /dev/ttyS1 for fictional SDF user mr_retro authenticating via PAP to tenex.org (the SDF radius server):

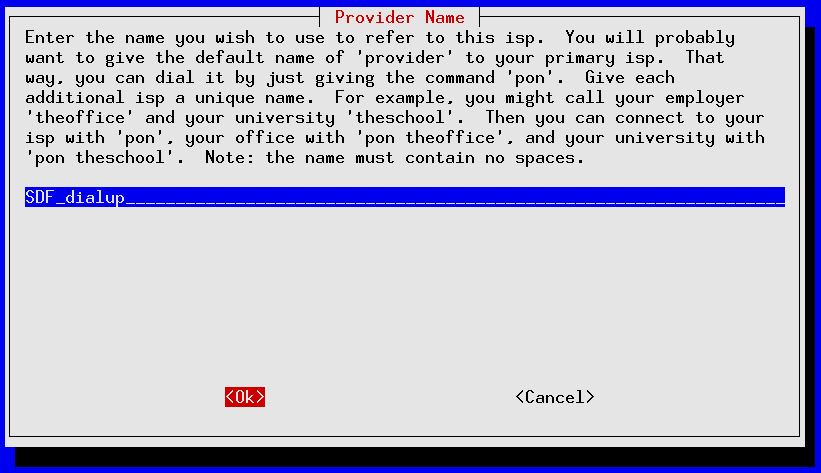
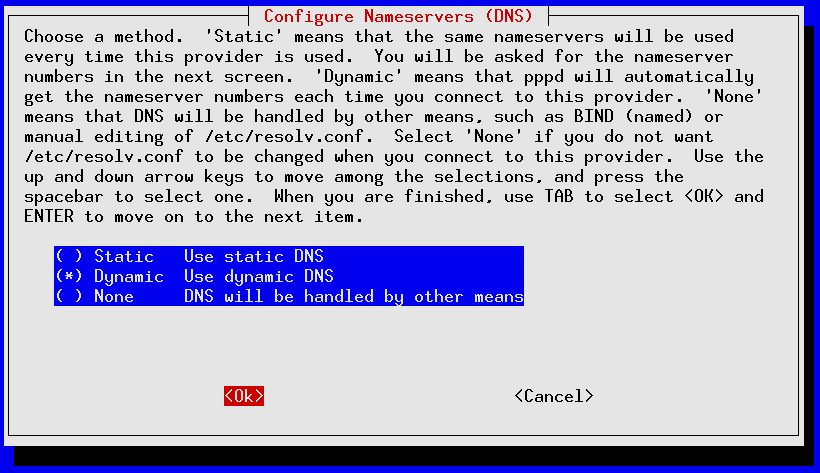
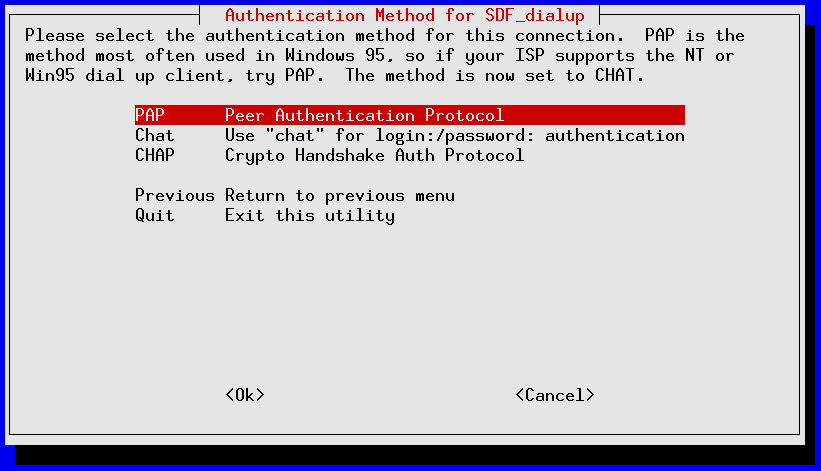
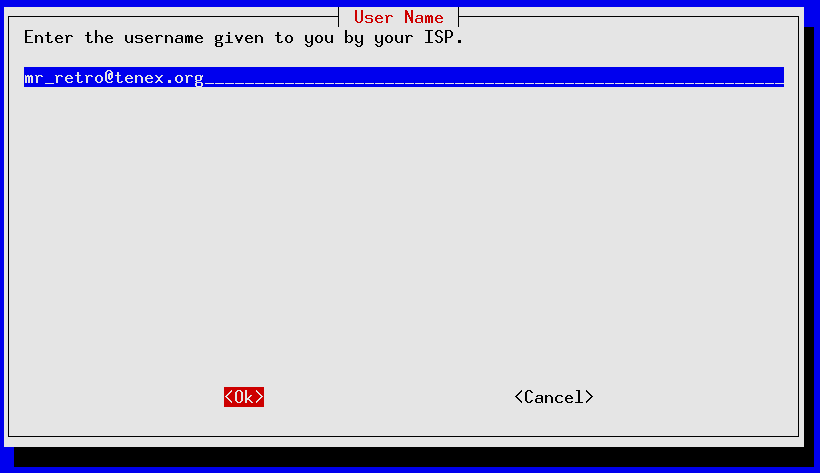
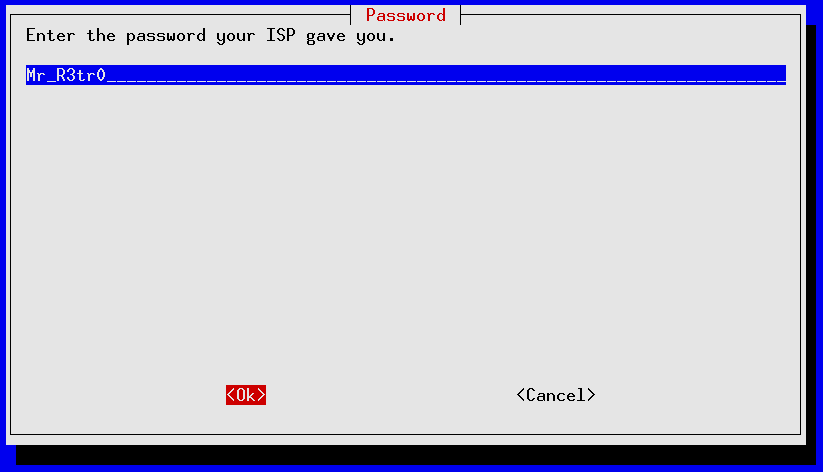
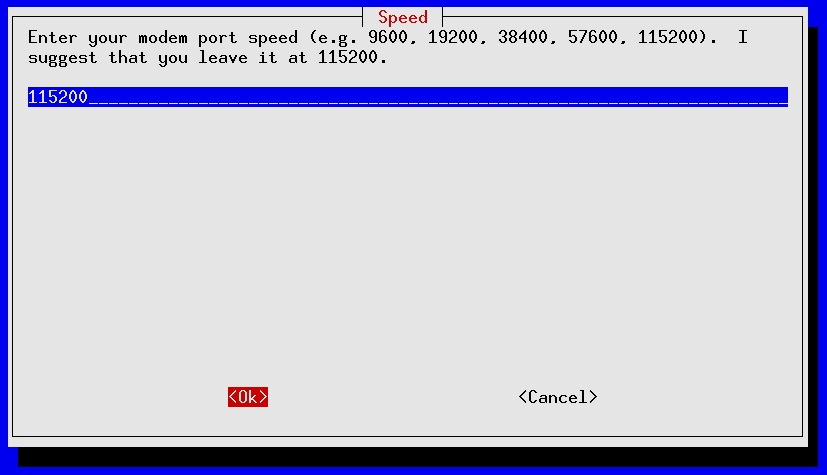
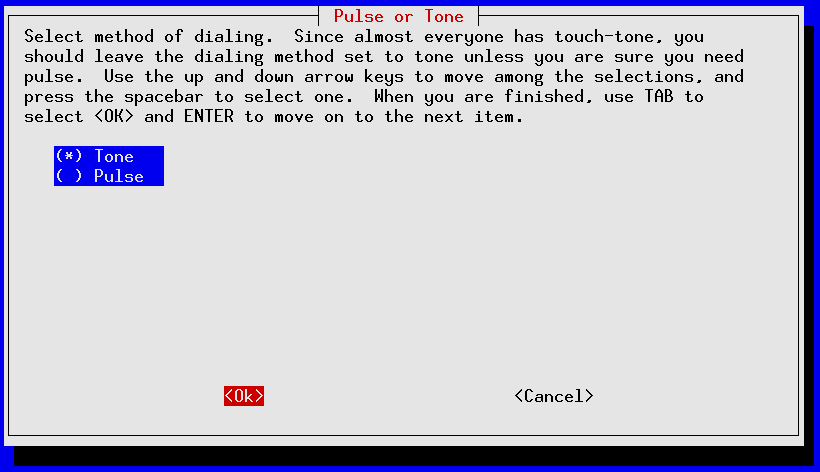
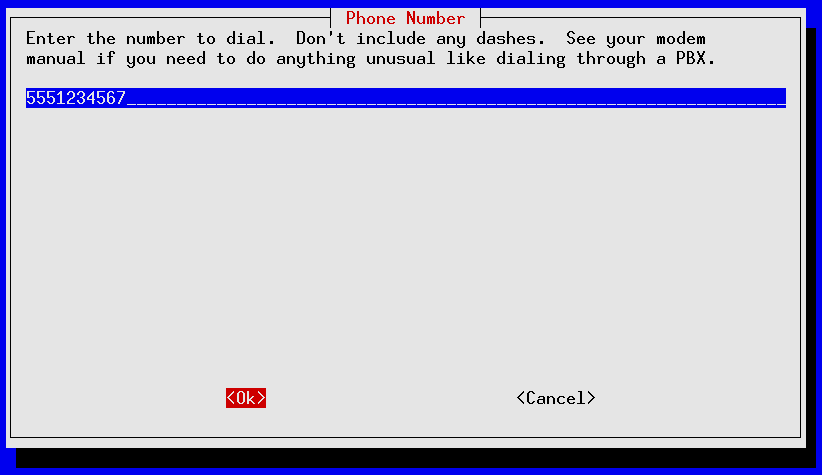

If you made a mistake anywhere you can re-start pppconfig and edit your newly created account. Use the “Advanced Options” for making tweaks to your modem's initialization settings.
Starting, Stopping and Monitoring the Dial-up Network Connection:
Startup:
pon gets your dial-up network connection going:
# mr_retro@rustbucket:~$ pon SDF_dialup
You should hear the modem initiating the handshake. If all goes well you should be connected; use ping to test:
# mr_retro@rustbucket:~$ ping -c1 sdf.org PING sdf.org (192.94.73.15) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from SDF.ORG (192.94.73.15): icmp_seq=1 ttl=248 time=72.7 ms --- sdf.org ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 72.726/72.726/72.726/0.000 ms
Monitoring:
plog provides a simple PPP log file interface. It accepts the same options as tail(1) ; use -f to provide an on-going dump of events in a separate terminal:
# mr_retro@rustbucket:~$ plog -f Jan 12 15:16:05 rustbucket pppd[2039]: pppd 2.4.5 started by mr_retro, uid 1001 Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: abort on (BUSY) Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: abort on (NO CARRIER) Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: abort on (VOICE) Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: abort on (NO DIALTONE) Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: abort on (NO DIAL TONE) Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: abort on (NO ANSWER) Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: abort on (DELAYED) Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: send (ATZ^M) Jan 12 15:16:06 rustbucket chat[2042]: expect (OK) Jan 12 15:16:08 rustbucket chat[2042]: ATZ^M^M Jan 12 15:16:08 rustbucket chat[2042]: OK Jan 12 15:16:08 rustbucket chat[2042]: -- got it Jan 12 15:16:08 rustbucket chat[2042]: send (ATDT5551234567^M) Jan 12 15:16:08 rustbucket chat[2042]: expect (CONNECT) Jan 12 15:16:08 rustbucket chat[2042]: ^M Jan 12 15:16:41 rustbucket chat[2042]: ATDT5551234567^M^M Jan 12 15:16:41 rustbucket chat[2042]: CONNECT Jan 12 15:16:41 rustbucket chat[2042]: -- got it Jan 12 15:16:41 rustbucket chat[2042]: send (\d) Jan 12 15:16:42 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Script /usr/sbin/chat -v -f /etc/chatscripts/SDF_dialup finished ... Jan 12 15:16:42 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Serial connection established. Jan 12 15:16:42 rustbucket pppd[2039]: using channel 6 Jan 12 15:16:42 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Using interface ppp0 Jan 12 15:16:42 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Connect: ppp0 <--> /dev/ttyS1 ...
Stopping:
poff shuts down your dial-up network connection:
# mr_retro@rustbucket:~$ poff SDF_dialup
You should hear the modem drop the connection ; verify with plog:
# mr_retro@rustbucket:~$ plog ... Jan 12 15:16:45 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Script /etc/ppp/ip-up finished (pid 2046), status = 0x0 Jan 12 15:30:18 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Terminating on signal 15 Jan 12 15:30:18 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Connect time 13.6 minutes. Jan 12 15:30:18 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Sent 39110 bytes, received 406951 bytes. Jan 12 15:30:18 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Script /etc/ppp/ip-down started (pid 2083) Jan 12 15:30:18 rustbucket pppd[2039]: sent [LCP TermReq id=0x2 "User request"] Jan 12 15:30:18 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Script /etc/ppp/ip-down finished (pid 2083), status = 0x0 Jan 12 15:30:18 rustbucket pppd[2039]: rcvd [LCP TermAck id=0x2] Jan 12 15:30:18 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Connection terminated. Jan 12 15:30:20 rustbucket pppd[2039]: Exit.
References:
- pppconfig(8) - configure pppd to connect to the Internet
- pon(1), poff(1), plog(1) – starts up, shuts down or lists the log of PPP connections
- Ubuntu Community Documentation – Ubuntu Dialup HowTo
Debian Linux Modem Configuration - Dial-up Modems
$Id: dialup_ubuntu.html,v 1.2 2011/01/16 09:43:09 jgw Exp $ SDF Dial-up via pppconfig and pon poff plog on Ubuntu - setup a PPP-based dial-up network connection on Linux
